Hydraulic Actuation
Hydraulically actuated brakes use fluid pressure to precisely control high braking forces. They are suitable for applications involving heavy loads and require reliable power delivery.
Pneumatic Actuation
Pneumatically actuated brakes operate using compressed air, offering fast response times and making them ideal for industrial applications that demand consistent, dynamic braking operations.
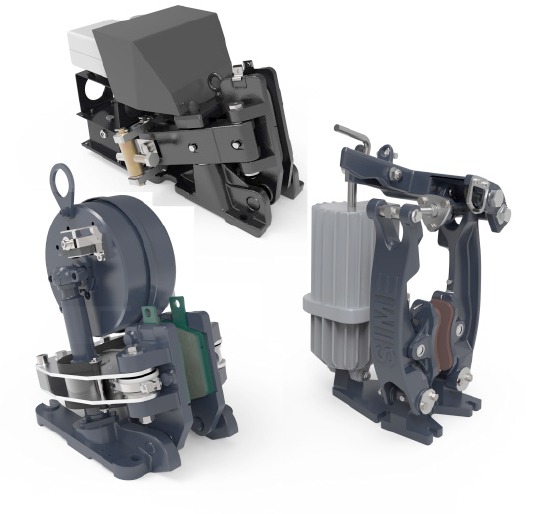

Electromagnetic
Electromagnetic brakes use magnetic fields to generate braking force without physical contact. They enable fast and accurate braking and are well-suited for energy-efficient and automated systems.
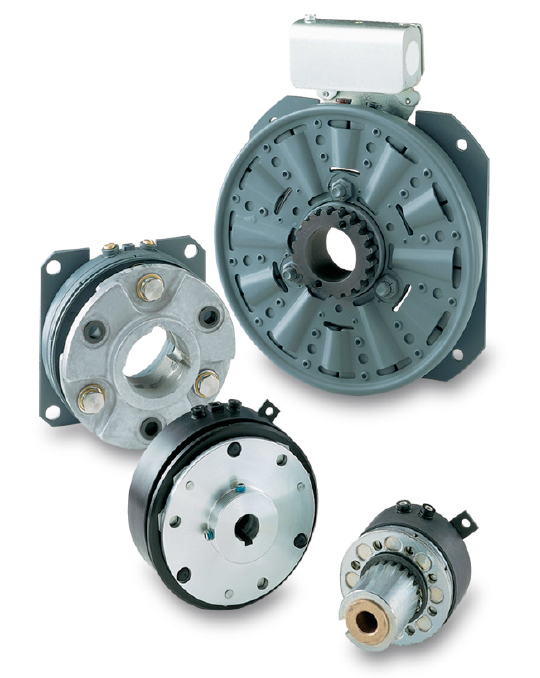

Water-Cooled Brakes
These brakes utilize water for cooling, providing efficient heat dissipation under intense operating conditions to prevent overheating and extend service life.
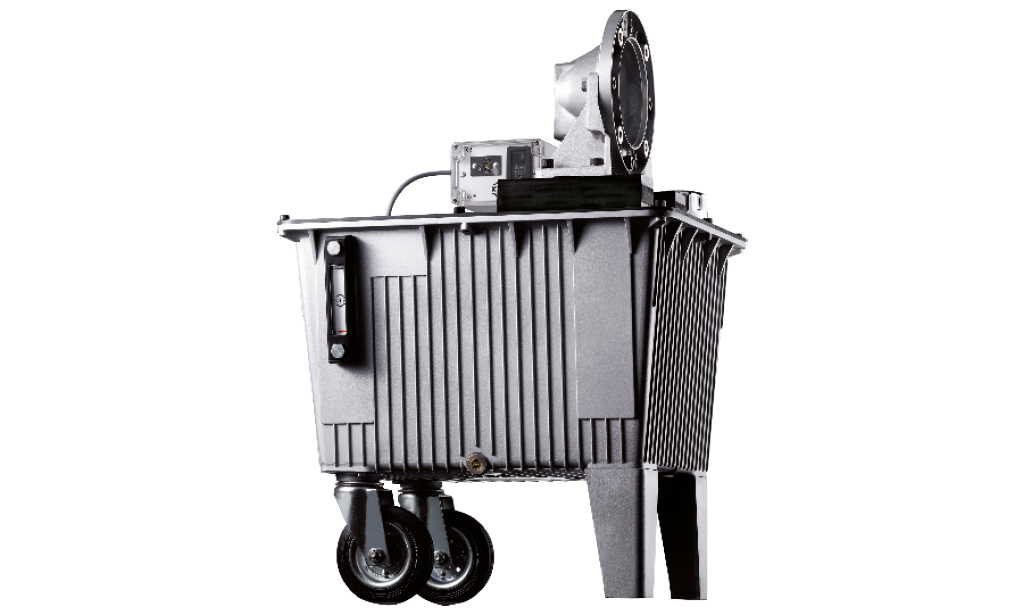

Cooling Systems
Cooling systems in brakes ensure effective temperature regulation and protect against thermal damage, thereby maximizing brake performance and service life.
Spring-Applied Brakes
Spring-applied brakes are engaged by spring force and released when external energy is supplied. They provide fail-safe functionality for emergency stops or power outages.
Emergency Stop Brakes
Emergency stop brakes ensure immediate halting of machinery in critical situations. They offer a high level of safety and protection during unexpected operational interruptions.
Dynamic Brakes
Dynamic brakes allow for continuous braking under varying speeds and loads. They deliver fast response times and high precision in demanding applications.













































